tsgettoolbox and tstoolbox - Command Line Interface¶
‘tsgettoolbox nwis …’: Download data from the National Water Information System (NWIS)¶
This notebook is to illustrate the command line usage for ‘tsgettoolbox’ and ‘tstoolbox’ to download and work with data from the National Water Information System (NWIS). There is a different notebook to do the same thing from within a Python program called tsgettoolbox-nwis-api.
First off, always nice to remind myself about the options. Each sub-command has their own options kept consistent with the options available from the source service. The way that NWIS works is you have one major filter and one or more minor filters to define what sites you want.
[ ]:
tsgettoolbox nwis_dv --help
Let’s say that I want flow (parameterCd=00060) for site ‘02325000’. I first make sure that I am getting what I want by allowing the output to be printed to the screen. Note the pipe (’|’) that directs output to the ‘head’ command to display the top 10 lines of the time-series.
[14]:
tsgettoolbox nwis_dv --sites 02325000 --startDT '2000-01-01' --parameterCd 00060 | head
Datetime,USGS-02325000-00060
2000-01-01,82
2000-01-02,81
2000-01-03,80
2000-01-04,79
2000-01-05,75
2000-01-06,75
2000-01-07,74
2000-01-08,73
2000-01-09,75
Then I redirect to a file with “> filename.csv” so that I don’t have to wait for the USGS NWIS services for the remaining work or analysis.
[15]:
tsgettoolbox nwis_dv --sites 02325000 --startDT '2000-01-01' --parameterCd 00060 > 02325000_flow.csv
‘tstoolbox …’: Process data using ‘tstoolbox’¶
Now lets use “tstoolbox” to plot the time-series. Note the redirection again, this time for input as “< filename.csv”. Default plot filename is “plot.png”.
[16]:
tstoolbox plot < 02325000_flow.csv
‘tstoolbox plot’ has many options that can be used to modify the plot.
[17]:
tstoolbox plot --help
usage: tstoolbox plot [-h] [--ofilename <str>] [--type <str>] [--xtitle <str>]
[--ytitle <str>] [--title <str>] [--figsize <str>] [--legend LEGEND]
[--legend_names <str>] [--subplots] [--sharex] [--sharey] [--style <str>]
[--logx] [--logy] [--xaxis <str>] [--yaxis <str>] [--xlim XLIM] [--ylim
YLIM] [--secondary_y] [--mark_right] [--scatter_matrix_diagonal <str>]
[--bootstrap_size BOOTSTRAP_SIZE] [--bootstrap_samples BOOTSTRAP_SAMPLES]
[--norm_xaxis] [--norm_yaxis] [--lognorm_xaxis] [--lognorm_yaxis]
[--xy_match_line <str>] [--grid GRID] [-i <str>] [-s <str>] [-e <str>]
[--label_rotation <int>] [--label_skip <int>] [--force_freq FORCE_FREQ]
[--drawstyle <str>] [--por] [--columns COLUMNS] [--invert_xaxis]
[--invert_yaxis] [--plotting_position <str>]
Plot data.
optional arguments:
-h | --help
show this help message and exit
--ofilename <str>
Output filename for the plot. Extension defines the type, ('.png').
Defaults to 'plot.png'.
--type <str>
The plot type. Defaults to 'time'.
Can be one of the following:
time
standard time series plot
xy
(x,y) plot, also know as a scatter plot
double_mass
(x,y) plot of the cumulative sum of x and y
boxplot
box extends from lower to upper quartile, with line at the median.
Depending on the statistics, the wiskers represent the range of
the data or 1.5 times the inter-quartile range (Q3 - Q1)
scatter_matrix
plots all columns against each other
lag_plot
indicates structure in the data
autocorrelation
plot autocorrelation
bootstrap
visually asses aspects of a data set by plotting random selections of
values
probability_density
sometime called kernel density estimation (KDE)
bar
sometimes called a column plot
barh
a horizontal bar plot
bar_stacked
sometimes called a stacked column
barh_stacked
a horizontal stacked bar plot
histogram
calculate and create a histogram plot
norm_xaxis
sort, calculate probabilities, and plot data against an x axis normal
distribution
norm_yaxis
sort, calculate probabilities, and plot data against an y axis normal
distribution
lognorm_xaxis
sort, calculate probabilities, and plot data against an x axis lognormal
distribution
lognorm_yaxis
sort, calculate probabilities, and plot data against an y axis lognormal
distribution
weibull_xaxis
sort, calculate and plot data against an x axis weibull distribution
weibull_yaxis
sort, calculate and plot data against an y axis weibull distribution
--xtitle <str>
Title of x-axis, default depend on type.
--ytitle <str>
Title of y-axis, default depend on type.
--title <str>
Title of chart, defaults to ''.
--figsize <str>
The 'width,height' of plot as inches. Defaults to '10,6.5'.
--legend LEGEND
Whether to display the legend. Defaults to True.
--legend_names <str>
Legend would normally use the time-series names associated with the input
data. The 'legend_names' option allows you to override the names in
the data set. You must supply a comma separated list of strings for
each time-series in the data set. Defaults to None.
--subplots
boolean, default False. Make separate subplots for each time series
--sharex
boolean, default True In case subplots=True, share x axis
--sharey
boolean, default False In case subplots=True, share y axis
--style <str>
Comma separated matplotlib style strings matplotlib line style per
time-series. Just combine codes in 'ColorLineMarker' order, for
example r--* is a red dashed line with star marker.
┌──────┬─────────┐
│ Code │ Color │
├──────┼─────────┤
│ b │ blue │
├──────┼─────────┤
│ g │ green │
├──────┼─────────┤
│ r │ red │
├──────┼─────────┤
│ c │ cyan │
├──────┼─────────┤
│ m │ magenta │
├──────┼─────────┤
│ y │ yellow │
├──────┼─────────┤
│ k │ black │
├──────┼─────────┤
│ w │ white │
╘══════╧═════════╛
┌─────────┬───────────┐
│ Number │ Color │
├─────────┼───────────┤
│ 0.75 │ 0.75 gray │
├─────────┼───────────┤
│ ...etc. │ │
╘═════════╧═══════════╛
┌──────────────────┐
│ HTML Color Names │
├──────────────────┤
│ red │
├──────────────────┤
│ burlywood │
├──────────────────┤
│ chartreuse │
├──────────────────┤
│ ...etc. │
╘══════════════════╛
Color reference: <http://matplotlib.org/api/colors_api.html>
┌──────┬──────────────┐
│ Code │ Lines │
├──────┼──────────────┤
│ • │ solid │
├──────┼──────────────┤
│ -- │ dashed │
├──────┼──────────────┤
│ -. │ dash_dot │
├──────┼──────────────┤
│ : │ dotted │
├──────┼──────────────┤
│ None │ draw nothing │
├──────┼──────────────┤
│ ' ' │ draw nothing │
├──────┼──────────────┤
│ '' │ draw nothing │
╘══════╧══════════════╛
Line reference: <http://matplotlib.org/api/artist_api.html>
┌──────┬────────────────┐
│ Code │ Markers │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ . │ point │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ o │ circle │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ v │ triangle down │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ ^ │ triangle up │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ < │ triangle left │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ > │ triangle right │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ 1 │ tri_down │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ 2 │ tri_up │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ 3 │ tri_left │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ 4 │ tri_right │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ 8 │ octagon │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ s │ square │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ p │ pentagon │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ • │ star │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ h │ hexagon1 │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ H │ hexagon2 │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ • │ plus │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ x │ x │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ D │ diamond │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ d │ thin diamond │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ _ │ hline │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ None │ nothing │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ ' ' │ nothing │
├──────┼────────────────┤
│ '' │ nothing │
╘══════╧════════════════╛
Marker reference: <http://matplotlib.org/api/markers_api.html>
--logx
DEPRECATED: use '--xaxis="log"' instead.
--logy
DEPRECATED: use '--yaxis="log"' instead.
--xaxis <str>
Defines the type of the xaxis. One of 'arithmetic', 'log'. Default is
'arithmetic'.
--yaxis <str>
Defines the type of the yaxis. One of 'arithmetic', 'log'. Default is
'arithmetic'.
--xlim XLIM
Comma separated lower and upper limits (--xlim 1,1000) Limits for the
x-axis. Default is based on range of x values.
--ylim YLIM
Comma separated lower and upper limits (--ylim 1,1000) Limits for the
y-axis. Default is based on range of y values.
--secondary_y
Boolean or sequence, default False Whether to plot on the secondary y-axis
If a list/tuple, which time-series to plot on secondary y-axis
--mark_right
Boolean, default True : When using a secondary_y axis, should the legend
label the axis of the various time-series automatically
--scatter_matrix_diagonal <str>
If plot type is 'scatter_matrix', this specifies the plot along the
diagonal. Defaults to 'probability_density'.
--bootstrap_size BOOTSTRAP_SIZE
The size of the random subset for 'bootstrap' plot. Defaults to 50.
--bootstrap_samples BOOTSTRAP_SAMPLES
The number of random subsets of 'bootstrap_size'. Defaults to 500.
--norm_xaxis
DEPRECATED: use '--type="norm_xaxis"' instead.
--norm_yaxis
DEPRECATED: use '--type="norm_yaxis"' instead.
--lognorm_xaxis
DEPRECATED: use '--type="lognorm_xaxis"' instead.
--lognorm_yaxis
DEPRECATED: use '--type="lognorm_yaxis"' instead.
--xy_match_line <str>
Will add a match line where x == y. Default is ''. Set to a line style
code.
--grid GRID
Boolean, default True Whether to plot grid lines on the major ticks.
-i <str> | --input_ts <str>
Filename with data in 'ISOdate,value' format or '-' for stdin.
-s <str> | --start_date <str>
The start_date of the series in ISOdatetime format, or 'None' for
beginning.
-e <str> | --end_date <str>
The end_date of the series in ISOdatetime format, or 'None' for end.
--label_rotation <int>
Rotation for major labels for bar plots.
--label_skip <int>
Skip for major labels for bar plots.
--force_freq FORCE_FREQ
Force this frequency for the plot. WARNING: you may lose data if not
careful with this option. In general, letting the algorithm
determine the frequency should always work, but this option will
override. Use PANDAS offset codes,
--drawstyle <str>
'default' connects the points with lines. The steps variants produce
step-plots. 'steps' is equivalent to 'steps-pre' and is maintained
for backward-compatibility. ACCEPTS:
['default' | 'steps' | 'steps-pre' | 'steps-mid' | 'steps-post']
--por
Plot from first good value to last good value. Strip NANs from beginning
and end.
--columns COLUMNS
Columns to pick out of input. Can use column names or column numbers. If
using numbers, column number 1 is the first data column. To pick
multiple columns; separate by commas with no spaces. As used in
'pick' command.
--invert_xaxis
Invert the x-axis.
--invert_yaxis
Invert the y-axis.
--plotting_position <str>
'weibull', 'benard', 'tukey', 'gumbel', 'hazen', 'cunnane', or
'california'. The default is 'weibull'.
┌────────────┬─────────────────┬───────────────────────┐
│ weibull │ i/(n+1) │ mean of sampling │
│ │ │ distribution │
├────────────┼─────────────────┼───────────────────────┤
│ benard │ (i-0.3)/(n+0.4) │ approx. median of │
│ │ │ sampling distribution │
├────────────┼─────────────────┼───────────────────────┤
│ tukey │ (i-1/3)/(n+1/3) │ approx. median of │
│ │ │ sampling distribution │
├────────────┼─────────────────┼───────────────────────┤
│ gumbel │ (i-1)/(n-1) │ mode of sampling │
│ │ │ distribution │
├────────────┼─────────────────┼───────────────────────┤
│ hazen │ (i-1/2)/n │ midpoints of n equal │
│ │ │ intervals │
├────────────┼─────────────────┼───────────────────────┤
│ cunnane │ (i-2/5)/(n+1/5) │ subjective │
├────────────┼─────────────────┼───────────────────────┤
│ california │ i/n │ │
╘════════════╧═════════════════╧═══════════════════════╛
Where 'i' is the sorted rank of the y value, and 'n' is the total number
of values to be plotted.
Only used for norm_xaxis, norm_yaxis, lognorm_xaxis, lognorm_yaxis,
weibull_xaxis, and weibull_yaxis.
[18]:
tstoolbox plot --ofilename flow.png --ytitle 'Flow (cfs)' --title '02325000: FENHOLLOWAY RIVER NEAR PERRY, FLA' --legend False < 02325000_flow.csv

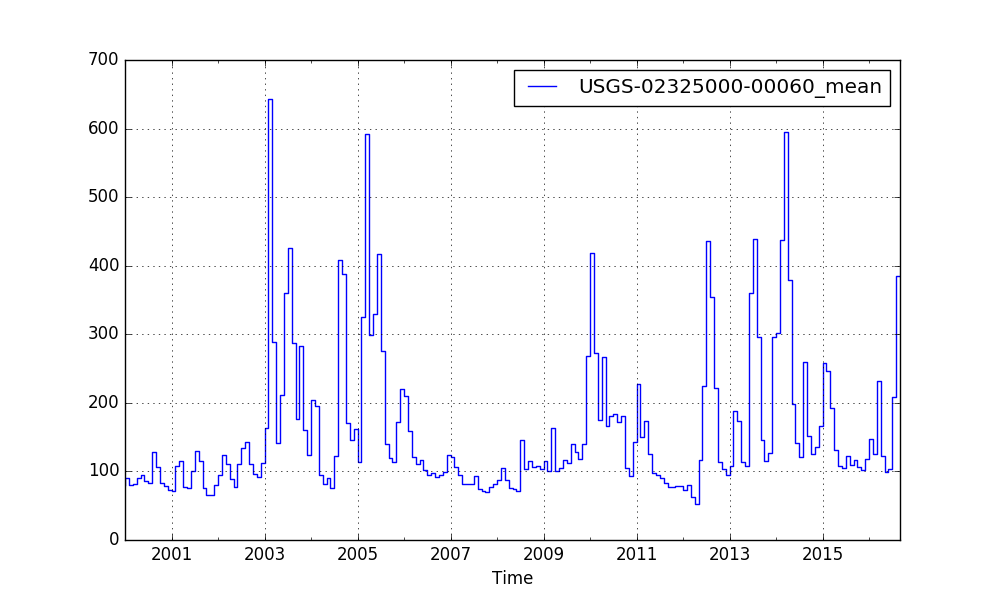
Monthly Average Flow¶
You can also use tstoolbox to make calculations on the time-series, for example to aggregate to monthly average flow:
[21]:
tstoolbox aggregate --groupby M --statistic mean < 02325000_flow.csv | head
Datetime,USGS-02325000-00060_mean
2000-01-31,80
2000-02-29,89.7931
2000-03-31,80.0323
2000-04-30,81.7667
2000-05-31,90.8387
2000-06-30,94.4
2000-07-31,85.9032
2000-08-31,83.0323
2000-09-30,128.067
[20]:
tstoolbox aggregate --groupby M --statistic mean < 02325000_flow.csv | tstoolbox plot --ofilename plot_monthly.png --drawstyle steps-pre

